Buy A Business In Canada For PR – Your Complete Guide
Canada is desirable for international business seekers looking for chances due to its thriving economy, stable political environment, and broad market. You want to buy a business in Canada for PR. If so, this guide is designed to give you helpful advice and a systematic way to work through the complexities of the Canadian business environment.
Foreign nationals who are considering buying a business in Canada must consider the requirements established by Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC). The IRCC oversees immigration to Canada, which includes the procedures involved in being a foreign investor and running a company. Most of the time, the outcome of the immigration application could depend on how well the firm is doing. The immigration status of Canadians and permanent residents can be positively impacted by proving the business’s viability and its capacity to contribute to Canada’s economic, cultural, or other competitive advantages.
To ensure legal compliance, secure the required immigration status, and increase the likelihood of a profitable business venture in Canada, considering IRCC standards is essential when purchasing a business there. It is advisable to do extensive study, comprehend the requirements of the immigration program you intend to apply for, and, if necessary, seek professional guidance.
Which business does IRCC like more?
Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) does not state clearly whose businesses it supports. However, it has immigration policies aimed at luring business owners, financiers, and skilled labourers who help boost the Canadian economy. The following industries and companies support the objectives of the IRCC and could be taken into consideration when evaluating immigration applications:
1. Innovative and Technology-Driven Businesses
Innovation and technology are highly valued in Canada. It might fit nicely with Canadian economic priorities if your company is involved in research and development, cutting-edge technologies, or both.
2. Clean Energy and Environmental Sustainability
Canada is dedicated to projects promoting clean energy and environmental sustainability. Companies prioritizing sustainable practices, green technology, and renewable energy may be seen favourably.
3. Biotechnology and Healthcare
In Canada, the biotechnology and healthcare industries are quite significant. Companies that support improvements in healthcare services, biotech inventions, or medical research may be encouraged.
4. Food processing and agribusiness
Canada‘s agriculture industry is robust. Enterprises engaged in agribusiness, food processing, and sustainable agricultural methods can complement Canada‘s environmental and economic goals.
5. Manufacturing and Export-Oriented Enterprises
Manufacturing firms, particularly those with an export-oriented orientation, have the potential to make a substantial economic contribution to Canada. This fits nicely with the nation’s plan to increase foreign trade.
6. Tourism and Hospitality
The Canadian economy depends heavily on the travel and hotel sector. Companies like hotels, restaurants, and travel agencies that support this industry’s expansion could be seen favorably.
7. Institutions of Higher Learning and Training
Businesses that support education and training, such language schools, VTCs, and organizations that foster skill development, are in line with Canada‘s focus on workforce development and education.
8. Consutructions and Infrastructure
Businesses engaged in engineering, construction, and infrastructure development can play a critical role in bolstering Canada‘s economic growth, as there are numerous ongoing infrastructure projects around the country.
9. The Creative and Cultural Industries
Canada is proud of its multiculturalism. Companies in the creative industries—such as those in music, cinema, design, and the arts—may receive assistance because they add to the cultural fabric of the nation.
10. Aerospace and Advanced Manufacturing
Canada boasts a robust aerospace sector. Companies in the advanced industrial sector, especially those in aerospace and associated technology, might appeal to immigration officials.
It’s crucial to remember that the requirements and qualifying criteria differ based on the immigration program you’re applying for. Entrepreneurs can investigate various avenues, such as the Canada Startup visa Program, Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs), and the C11 work prmit. You can better grasp the intricacies of these programs and receive guidance through the application process by speaking with a Registered Canadian Immigration Consultant (RCIC) or legal experts, depending on your business type and objectives.
Which business doesn’t IRCC like?
The Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) does not state clearly that it is against any particular company. Nonetheless, applying for immigration programs may provide difficulties for some businesses or circumstances. To properly handle possible issues, one must be aware of them. The following elements should be considered cautiously:
1. Low-Skill or Low-Wage Businesses
Companies that provide low-wage jobs and mostly rely on low-skilled labour may require assistance. The immigration laws in Canada give preference to businesses that hire competent individuals and stimulate economic growth.
2. Speculative Businesses
Companies that are thought to be high-risk or speculative may face challenges. Immigration authorities favour companies demonstrating longevity and profitability through a well-defined, workable business plan.
3. Companies with Limited Growth Potential
Immigration authorities may find a business less appealing if it is in a declining industry or has limited room for expansion. Canada is looking for entrepreneurs that can help with job creation and economic development.
4. Non-Compliance with Canadian legislation
During the immigration examination process, businesses with a history of non-compliance with Canadian legislation, such as taxes, labour laws, or environmental regulations, may voice concerns.
5. Businesses with Ethical or Environmental Concerns
Industries or businesses with unethical or environmental concerns may come under investigation. In Canada, ethical and sustainable business practices are highly valued.
6. Oversaturated Markets
Launching a company in an oversaturated market or where there is fierce competition may make investors doubt the venture’s viability and success.
7. Companies That Don't Share Canadian Values
It shall not be accepted to be involved in any unlawful activity or company contravening Canadian laws.
8. Companies Involved in Illegal Activity
It shall not be accepted to be involved in any unlawful activity or company contravening Canadian laws.
9. Franchise Companies with Just a Little Autonomy
Given that the capacity to actively manage the business is frequently a critical component, several immigration programs may be wary of franchise enterprises where the investor has little control or authority over decisions.
It is significant to remember that every case is different and that firms are evaluated for immigration reasons using various criteria. Immigration programs may have different qualifying requirements, and companies must be able to show that they follow the law and ethical standards and contribute to the Canadian economy by creating jobs. To successfully negotiate the complexities of the immigration procedure, it is advisable to consult with legal specialists or a Registered Canadian Immigration Consultant (RCIC).
The requirement to buy a business in Canada for PR
To buy a business in Canada for PR (Permanent resident), there aren’t specific requirements solely related to your immigration status. However, buying a business in Canada entails several actions and factors. The requirements may change based on the industry, geography, and other variables. Here is a broad overview to assist you in comprehending the necessary conditions:
1. Ownership and Legal Framework
Choose the business’s legal structure (corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship, for example). Establish the ownership structure, particularly if starting a joint venture or partnership.
2. Business Appraisal
Analyze the company’s fair market value. This may entail doing a financial analysis, reviewing the assets and obligations, and estimating future earnings.
3. Exercise Due Diligence
Perform comprehensive due diligence to look at the company’s operational, legal, and financial elements. This may be necessary to examine contracts, financial statements, tax records, and other pertinent documents.
4. Legal Assistance
Hire attorneys to assist with the purchasing process. They can help with contract design or review, regulatory compliance checks, and legal assistance.
5. Financial Support
Obtain funding if required. This could entail borrowing money from personal resources, investing, or getting a company loan. Financial institutions could require a strong business plan in addition to the loan application.
6. Purchase agreement and negotiation
Discuss the conditions of the transaction with the vendor. A formal purchase agreement with all terms and conditions of the transaction should be established once an agreement is reached.
7. Registration of Businesses
Obtain a business registration from the relevant authorities. Getting a Business Number (BN) with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and registering with regional or local authorities may be necessary.
8. Transfer of Contracts and Assets
Assist with the transfer of contracts, licenses, and other authorizations required for the business’s operations.
9. Employee Transition
Consider the change’s effects on the company’s staff members, if any. Employment contracts, benefits, and other HR-related issues need to be addressed.
10. Tax Considerations
Recognize how the business purchase will affect your taxes. Maximizing your financial situation and ensuring compliance with tax rules may need consulting with an accountant.
11. Regulation Compliance
Ensure the company complies with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations pertaining to the industry and any standards about the environment, health, and safety.
12. Closing and Post-Closing Obligations
According to the conditions specified in the purchase agreement, close the transaction. Attend to any post-closing commitments, like agreements for training or consultation with the seller.
It is imperative to obtain professional guidance, including legal, financial, and maybe industry-specific knowledge throughout the process. You can effectively manage the challenges of purchasing a business by seeking advice from brokers, accountants, and attorneys knowledgeable in the Canadian business environment.
Advantages & Disadvantages of buying a business in Canada as a foreigner
Selecting the right business involves thorough research, self-reflection, and professional guidance. By following these steps, you can increase the likelihood of choosing a business that aligns with your goals and has the potential for long-term success.
Buying a business in Canada as a foreigner, like any business decision, comes with advantages and disadvantages. It’s essential to thoroughly research and consider various factors before investing significantly. Here are some general benefit and risk:
Advantages of buying a business in Canada for PR
- Infrastructure Already in Place: Purchasing an established company frequently includes infrastructure, including real estate, clientele, and operational procedures. When opposed to launching a business from scratch, this can save time and money.
- Developed Reputation and Brand: An established company may already have a reputation and brand. This might give you a good start in terms of honesty and trust.
- Revenue and Cash Flow: Operating businesses often immediately produce revenue and cash flow. Those who prefer a faster return on investment than launching a new company may find this advantageous.
- Skilled Staff: Purchasing a company frequently entails taking over a skilled and knowledgeable labour force, which is advantageous for the smooth running of the company.
- Current Clientele: An enterprise with a well-established clientele can offer a steadier flow of income and experience expansion via enhanced advertising and client retention tactics.
- Financing Opportunities: Since lenders may view an established company as less hazardous than a startup, financing a business purchase could be simpler than obtaining capital for a new venture.
Disadvantages of buying a business for PR
- Cost: Purchasing a well-established company might be costly. The purchase price, legal fees, due diligence costs, and any unanticipated liabilities could all be included in the price.
- Inherited Problems: The company you want to buy a business in Canada for PR might already deal with issues or obstacles that take time to surface. Finding any possible problems requires careful investigation.
- Mismatched Culture: There can be a cultural mismatch between your management style, objectives, or values and the current business. It can be challenging to bring disparate organizational cultures into harmony.
- Restricted Flexibility: When you buy an established company, contracts, organizational structure, and procedures are transferred to you. This could make carrying out your idea more challenging or making significant changes without encountering opposition.
- Market Shifts: Economic or industry shifts may impact the acquired company’s performance. Challenges may also arise from external reasons like regulation changes or technological developments.
- Hidden Liabilities: Even with careful diligence, the company may have unreported debts, unresolved legal matters, or unanticipated financial difficulties.
Collaborating closely with legal (RCIC, business lawyer, etc.) and financial experts (Accountant) is vital, as is carrying out extensive due diligence and carefully assessing how well the business fits your objectives and skills before deciding.
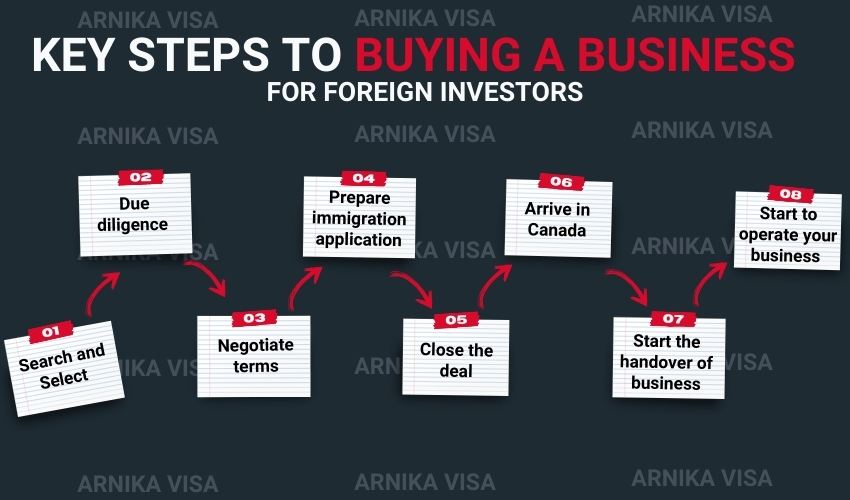
How to Buy a business in Canada?
A vital first step in assuring a successful endeavour is conducting adequate research and choosing the appropriate business. Here is a thorough how-to to get you through the process of buy a business in Canada for PR:
1. Self-Evaluation
- Interests and abilities: List your hobbies, areas of expertise, and skills. Pick a line of work that supports your enthusiasm and allows you to play to your advantage.
- Goals and Objectives: Clearly state your company’s short- and long-term objectives. Think about things like your goals for your money, your work-life balance, and your level of personal satisfaction.
2. Analysis of Markets
- Analyze different industries to learn about their growth potential, current trends, and obstacles. Choose industries that share your interests and have a promising future for the market.
- Determine Who Your Target Audience Is: Recognize their wants, needs, and habits to ensure your company satisfies consumer requests.
3. Regulatory and Legal Aspects:
- Legal form: Based on your preferences and the regulations in the jurisdiction of your choice, choose the legal form of your company (sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation).
- Regulatory Compliance: Learn about and comprehend the rules and specifications that apply to your industry. Make sure your company stays
4. Evaluation of Finances:
- Budgeting: Establish how much money you’ll need to launch and maintain your firm. Consider the startup cost, ongoing expenses, and possible funding sources.
- Establishing your income model is the first step: Ensure your firm is financially sustainable by understanding how it will make money.
5. SWOT Analysis:
- Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) Analysis: To evaluate the possibilities, threats, and internal and external strengths and weaknesses of your company, do a SWOT analysis. This research thoroughly explains where your company stands in the marketplace.
6. Due Diligence on Existing Businesses:
- Evaluate Opportunities: Assessing Possibilities: Do your research before picking an established company. Examine the company’s cash flow, clientele, standing, and potential operational or legal problems.
- Talk to Current Owners: Talk to the current owners to learn more about the opportunities, challenges, and day-to-day operations.
7. Long-Term Viability and Scalability:
- Scalability: Consider whether the company has room for growth and expansion. Consider scalability elements, including market demand, production capacity, and geographic reach.
- Adaptability: Make sure the company can change to keep up with emerging technologies and shifting market conditions.
8. Industry Networking:
- Industry Associations: Participate in networking events, join pertinent industry associations, and network with other professionals. Networking offers insightful information and cooperative opportunities.
9. Location Considerations:
- Geographic aspects: Consider the location of your company. Examine variables like the local economy’s state, competition level, and supplier and customer accessibility.
10. Risk Management:
- Identify Risks: Make a clear list of all possible dangers related to the company. Create a risk management strategy to reduce these risks and guarantee business continuity.
11. Professional Guidance:
- Seek professional guidance: Consulting experts, such as accountants, lawyers, and business consultants, for help. Their knowledge can assist you in making wise choices and avoiding typical mistakes.
12. Test the Market:
- Pilot or Beta Testing: Before committing entirely, consider testing your business idea on a smaller scale. This can offer insightful comments and analysis from actual clients.
13. Evaluate Your Decision:
- Think Back and Reevaluate: Give your research and decision-making process some thought. Considering fresh facts or evolving conditions, reevaluate your decision.
Steps for buying a business in Canada
To start a business in Canada as a foreigner, you must learn about the legal requirements, decide on a business structure, register your company, get the required permits, and consider the tax consequences. Create a business plan, establish a network, and obtain funding. Seek expert counsel and use tools like the Canada Business Network for direction.
1. Understanding the Canadian Business Environment
Canada continuously ranks highly for ease of business and has a strong and stable business environment. Learn about the Canadian economy, market trends, and legal system before you set out on your tour. Do extensive market research to find industries with room for expansion and match your hobbies and areas of competence.
2. Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Recognizing the legal and regulatory standards is essential before entering the Canadian market. Legal experts on Canadian business law should be consulted as each province and territory may have different business legislation. Industry-specific standards, employment laws, taxation, and corporate structures are essential factors to consider.
3. Obtaining Expert Advice
Experts like business brokers, attorneys, and accountants can greatly expedite purchasing. An RCIC, or Registered Canadian Immigration Consultant, can offer:
- Excellent support in navigating the immigration system.
- Guaranteeing adherence to immigration regulations.
- Assisting you with your business endeavour in Canada.
4. Work permits and immigration
International entrepreneurs need to comprehend the immigration process. The Canadian government provides investors and entrepreneurs with a range of immigration options. Depending on your company objectives and preferred location, carefully collaborate with your RCIC to investigate possibilities like the Canada Start-up Visa Program, Provincial Nominee Program (PNP), or the Express Entry system.
5. Due Diligence on Business Opportunities
When purchasing a business, extensive due diligence is necessary. Consider factors such as client base, market positioning, financial performance, and growth prospects while evaluating possible opportunities. Talk with the present owner to learn more about the company’s background, difficulties, and future growth prospects.
6. Financing Options for Foreign Entrepreneurs
Financial institutions in Canada offer a range of financing alternatives to business owners. Consider government subsidies, venture capital, and business loans to encourage foreign investment. A solid financial base guarantees your new business a seamless launch and long-term success.
7. Cultural Aspects and Market Adjustment
Your ability to succeed in Canadian corporate culture depends on it. Develop connections with regional stakeholders, connect with colleagues in the field, and modify your company plans to suit the tastes of Canadian customers. A strong local presence can help you blend in with the Canadian business community more efficiently and increase credibility.
8. Financial Compliance and Taxes
Following Canadian tax laws is very important. To fully comprehend your tax responsibilities, including payroll taxes, sales tax (GST/HST), and corporate income tax, work with knowledgeable accountants. Following financial compliance will help your company succeed in Canada over the long run by preventing legal problems.
9. Building a Skilled Workforce
Acquiring talent is essential to the success of any organization. Make use of Canada‘s talented and diversified labour pool by hiring locally. Recognize the ins and outs of the labor market, employment laws, and workplace culture and practices.
10. Marketing and Branding Strategies
Create a strong marketing plan to launch your company in the Canadian market. Use social media, local advertising outlets, and digital marketing to reach your target demographic. Adapt your branding to appeal to Canadian customers by stressing virtues like excellence, diversity, and involvement in the community.
11. Monitoring and Adapting to Market Trends
Keep up with consumer trends and market developments. Review your business plans frequently, adjust to shifting market conditions, and pursue new ideas to stay competitive. To maintain ties with the business community, become involved with associations for your industry and go to networking functions.
What are most profitable business in Canada?
A company’s profitability can be influenced by several variables, such as market demand, industry trends, geographic location, and the buyer’s interests and skill set. Nonetheless, the following broad categories of industries have demonstrated the most profitable business in Canada:
Food and Beverage
Cafes, restaurants, and catering companies can profit, mainly if they provide distinctive or superior dining experiences.
Health and Wellness
As individuals become more health-conscious, there is a growing demand for fitness centers, wellness spas, and health-related services.
E-commerce
With the growing popularity of online shopping, it might be profitable to launch or buy an e-commerce company. This can entail offering specialized services or making goods sales online.
Technology and IT Services
As digitalization spreads, companies providing software development, cybersecurity, IT consulting, and other technology services will find increased demand.
Home Renovation and Construction
The Canadian real estate market has created opportunities for construction and home remodelling companies.
Individual Services
Profitable ventures include those offering personal services like housekeeping, tutoring, pet care, and arranging your home.
Medical Services
The aging population drives demand for healthcare-related services such as home healthcare, senior care, and specialty medical services.
Franchises
Purchasing a well-known franchise with a tested business plan can be financially advantageous because these investments frequently include assistance and established brand awareness.
Environmental and Renewable Energy
With the focus on sustainability increasing, companies offering eco-friendly goods and services, waste management, and renewable energy can make money.
Education and Training
Offering specialized training or education services, both online and in-person, can be advantageous, particularly in niche markets.
Tourism and Hospitality
Businesses in tourist attractions, such as hotels, bed and breakfasts, and travel-related services, can be successful in areas with a strong tourism industry.
Automotive Services
In places with a high concentration of automobile owners, auto repair businesses, car detailing services, and specialist automotive services can be profitable.
It’s critical to conduct in-depth market research, evaluate the competitors, and comprehend industry trends before acquiring any organization. To ensure you are a good fit for the business you are considering, consider your abilities, passions, and background. Before purchasing, speaking with financial experts, industry experts, and business advisers can offer insightful advice. Remember that trends and economic conditions might change, so it’s best to do current research.
Immigration Pathway for buying a business in Canada as a foreigner
In Canada, there needs to be a program designed specifically for acquiring permanent residence through buying a business in Canada as a foreigner. To gain residency while actively managing or investing in a business, entrepreneurs and investors might investigate various immigration procedures. These initiatives frequently aim to draw in business-savvy people who can boost the Canadian economy. The following are some broad ideas and possible directions to consider:
Under the Entrepreneur Immigration Programs offered by certain Canadian provinces, people can become permanent residents by establishing or acquiring a business. Every province has its standards and demands. The Ontario Immigrant Nominee Program (OINP) Entrepreneur Stream and the British Columbia Provincial Nominee Program (BC PNP) Entrepreneur Immigration Stream are two examples.
2- C11 work permit
While not a traditional immigration program (Owner-Operator LMIA), this pathway enables you to buy a business in Canada for PR or start a business in Canada and apply for a work permit as an owner-operator. You must be actively involved in the company’s operation, and it must create jobs for Canadians.
3- Owner-Operator LMIA (Labour Market Impact Assessment)
Business owners may consider the Owner-Operator LMIA pathway in some instances. This entails purchasing or starting a company, after which the owner-operator must apply for a work visa. You can investigate options for permanent residency once you’re in Canada.
This program is for people who can contribute substantially to Canadian culture or sport and have relevant field experience. You must show that your endeavours will substantially impact Canada’s artistic or athletic life, that you want to work for yourself in the country, and that you meet the requirements.
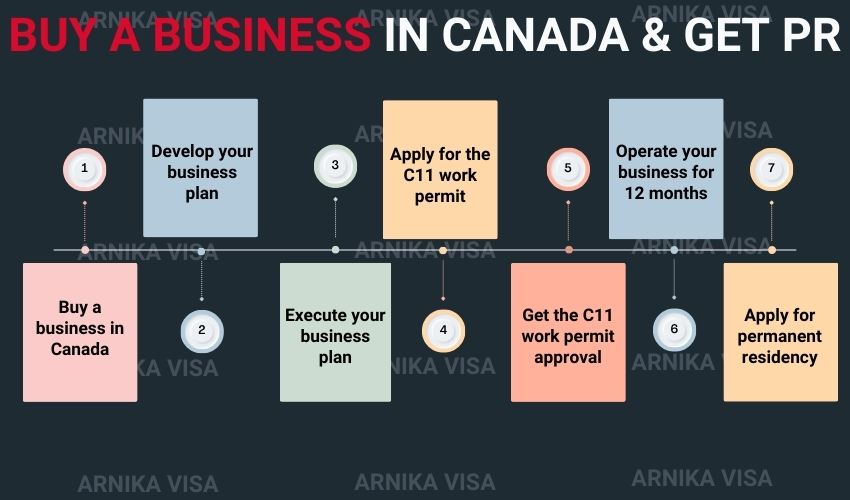
How to apply for business immigration to Canada
1. Research Immigration Programs:
Choose the one that best suits your intentions to Buy a business in Canada for PR. Examine the prerequisites and eligibility requirements for that particular program.
2. Business Selection
Select a company to buy a business in Canada for PR that satisfies the requirements of the chosen immigration scheme. Make sure your experience and skills fit with the company’s needs and that it is financially sustainable.
3. Due Diligence
Investigate the company thoroughly to determine its suitability, legal status, and financial stability.
4. Application Process
Comply with the procedures specified in the immigration program of your choice. Usually, this entails submitting a formal application or an Expression of Interest (EOI).
5. Business Plan:
Draft a thorough business plan explaining your company goals, including how you want it to be managed and flourish.
6. Nomination or Approval
Obtain from the immigration authorities the necessary nominations from the province, if any.
7. Permanent Residency
If approved, you might be given permanent residency in Canada, letting you live and work.
It’s crucial to remember that new initiatives and changes to immigration laws are possible. Consequently, for current and customized counsel based on your unique situation, it’s best to speak with an immigration lawyer or a licensed immigration consultant. To guarantee a seamless transition and compliance with pertinent rules, involving legal and financial experts during the business acquisition is essential.
Conclusion
Buying a business in Canada as a foreign entrepreneur offers many development and success prospects. Through comprehension of the legal, regulatory, and cultural subtleties and the pursuit of expert advice, you can adeptly maneuver through the Canadian business environment. This thorough manual acts as a road map and provides insightful information to assist you in making decisions and starting a profitable business venture in the Great White North.
How We Can Help with Buying a Business in Canada?
In my capacity as a Registered Canadian Immigration Consultant (RCIC), we are a vital resource for clients looking to buy a business in Canada for PR. We help by providing all-encompassing support, starting with carefully assessing their eligibility for business-ownership-related immigration programs. Our role is facilitating compliance and ensuring a seamless transition by offering insights into legal and regulatory requirements.
Among the services we offer are market research and discovering potential business prospects that fit the objectives of our clients and the conditions of the Canadian market. We assist clients in conducting due diligence on possible companies, assisting them in determining their potential for growth and financial stability.
I assist in obtaining the required visas and permits by navigating immigration channels and ensuring Canadian immigration laws are followed. Furthermore, we cooperate with financial and legal experts for a smooth transition.
In the process, we assign customers the knowledge they need to make educated decisions, provide strategic counsel, and streamline administrative procedures—all of which help to ensure their successful integration into the Canadian business scene.
Buying a business in Canada Related Articles
- Buying a Business in Canada for PR – Complete Guide
- How Much Money Is Required To Buy A Business In Canada?
- How To Buy A Business In Canada?
- The Most Profitable Business In Canada
- Canadian Immigration Business Plan
- How To Get A Business Visa To Canada?
- C11 Work Permit Canada – The Complete Guide To Apply






Hi, I am planning to apply via C11 work permit. I intend to buy a business in Canada with significant benefits in healthcare. I will incorporate in Ontario: 1. Do I need to offer myself employment as CEO by registering at the Employers Portal to fulfill the eligibility requirements? 2. Any advice on processing my family (spouse and two children, 16 and 18 years) to get visa approval? Thank you
1- Registering as CEO and offering a job strengthens your C11 work permit application, demonstrating your role in the business. 2- Ensure thorough documentation, including proof of familial relationship and financial support. Highlight the benefits your business brings to Canada. Professional guidance can streamline the process and increase approval chances.
The primary objective of investing in Canada is for business investments, business developments, and business expansions under Infrastructure development programs & projects in urban-rural areas. I was a PR of Canada from 1990-1998, wherein I did my education and job & had a business in Ontario. I am looking at the C11 work permit option. Can I buy a business in this category? Thanks for your guidance
Given your prior residency and business experience in Canada, pursuing the C11 work permit for business investments aligns with your objectives. Your background strengthens your case. We can guide you through the application process, ensuring compliance and maximizing investment opportunities. Let’s tackle this journey together.
Hello, I have been a director and senior executive of a company (Care Home Service provider) in Europe for over three years, which is doing well. I have had a small Ontario-incorporated company in Canada for over three years – Care Support and Home Support work activities, which are not doing well currently due to the lack of my presence. I need to grow this business. However, I can show $70,000 in a Canadian bank to support the company if I am present here. My English is good, and I can get 6 in IELTS. My age is 52. Between an ICT work permit and a C11 work permit, which one is more suitable for me to get PR? How many Canadian staff members must be recruited for ICT and C11 work permit visas? What documents are needed for them? Thanks
Both ICT and C11 permits offer paths to PR. ICT suits multinational transfers, while C11 is for business establishments. ICT may not require Canadian staff, but C11 likely does. Documents include qualifications, business plans, and financial statements. Consult an immigration expert for tailored guidance. Good luck!
I plan to buy an IT company and apply for a C11 work permit for myself as CEO. Let me know how I can proceed.
“Incorporate your IT company in Canada. Developing a strong business plan shows significant benefits for Canadians or Canada. Apply for a C11 work permit as CEO. Ensure compliance with immigration regulations. Seek professional guidance from an expert on C11 visas if needed. Good luck!”
I am looking for assistance with a C11 work permit. The Business is an Australian-Canadian consultation agency. I am an Australian business consultant. The Canadian branch was established in November 2022. I am currently holding an IEC visa expiring in late September 2024. Please let me know how to apply.
Explore extending your stay or transitioning to a proper Canadian work permit. Contact us for personalized guidance on your application process.
I want to purchase a business in Canada and move to Canada with my family with PR. What program will I be eligible for, and how much will the government and your fees be?
Depending on your situation, you may be eligible for various business immigration programs like the Start-Up Visa or the Provincial Nominee Program. Our fees vary based on services required. Let’s schedule a consultation to discuss your specific needs and costs involved.
I want to purchase a business in Canada and move to Canada with my family with PR. What program will I be eligible for, and how much government and your fees will be?
Depending on your situation, you may be eligible for various business immigration programs like the Start-Up Visa or the Provincial Nominee Program. Our fees vary based on services required. Let’s schedule a consultation to discuss your specific needs and costs involved.
I’m selling a business that also includes an apartment in B.C. and would like to advertise.
Thank you for considering our services. We specialize in business immigration to Canada. Please provide details about your business in B.C. for tailored advertising. Let’s discuss how we can assist you in showcasing your offering to potential buyers.
I am on a visitor visa in Canada. I am a qualified engineer with more than 25 years of experience, and I am looking for a C11 visa to buy a business as an entrepreneur and settle here.
As a visitor in Canada, you’ll need to make sure that you are eligible to apply for C11 work permit inside Canada. The transition to a suitable work permit type like the C11 visa to work as an entrepreneur. Ensure your business plan meets program criteria, secure support from community you would like to open a business, and comply with immigration regulations to enhance your chances of approval.
I have a few questions regarding buying an already-established business. I need to know the procedure and how it works. Please let me know if we can set up an online meeting. Also, is there any opportunity to buy a partnership?
To buy an established business, research, conduct due diligence, negotiate terms, seek legal and financial advice, and finalize the sale. For the C11 visa, ensure eligibility, prepare documents, apply, undergo assessment, and receive the visa to start or buy a business in Canada if approved. Fortunately, all of our consultation sessions are held online.
We are operating a tour and travel business here in Pakistan. We are interested in getting PR over this business. I have studied the details of the c11 work permit category on your website. I am interested in the same or buy one. So please send the details.
For your travel agency business plan, include a business description, market analysis, marketing and sales plans, operational details, team overview, financial projections, and risk analysis. Is there any specific section of the business plan you’d like to focus on or need further assistance with? Let us know, and we’ll be happy to help!
To apply for Canadian PR through the C11 work permit for your tour business, prepare the required documents and apply for your C11 visa. Get the work permit, operate your business in Canada, then follow immigration procedures to apply for PR through Express Entry or a Provincial Nominee Program.
I have a diploma in electronic with a license for 15 years and have 3 technical degrees in plumbing. Am I eligible to start my business in Canada? Please guide me.
Yes, you may be eligible to start a business in Canada. Depending on your background and business plans, programs like the Start-Up Visa or provincial entrepreneur programs might suit you. Consult a business immigration lawyer to explore your options and receive personalized guidance.
Hi. Recently I’ve been inhibited from entering Canada as a worker. My employer had voided the LMIA, however I proceeded to book flight and coming to Canada. I was wondering that if this record will affect my future Visa application investigation process negatively.
In fact I am thinking of starting a new way of entering Canada through buying a business. I am 50 years old and haven’t had any business in my country yet. I used to work as a medical lab technician and now I’m retired. My previous job offer was in pizza cook position which was voided by employer prior to my arrival to Canada.
And finally I would like to be counseled about a suitable way of application.
Being denied entry due to a void LMIA may be noted in your immigration history, but it doesn’t automatically prevent future applications. Since you’re considering business immigration without prior ownership experience, pathways like the Entrepreneur or Provincial Nominee Programs may be challenging but possible if you can demonstrate investment funds, management ability, and a clear business plan. At your age and background, exploring self-employed or investor options could be more suitable than employer-driven permits.