Starting a business in Canada
Starting a business in Canada requires various amounts of capital depending on several factors, including the type of business, location, industry, and size of the operation.
Embarking on a business journey in Canada is not just a promising venture, but a potentially rewarding one, given the country’s stable economy and supportive business environment. The following steps and insights will guide you, whether you are a resident or an international entrepreneur, toward a path of success.
How to Start a Business in Canada?
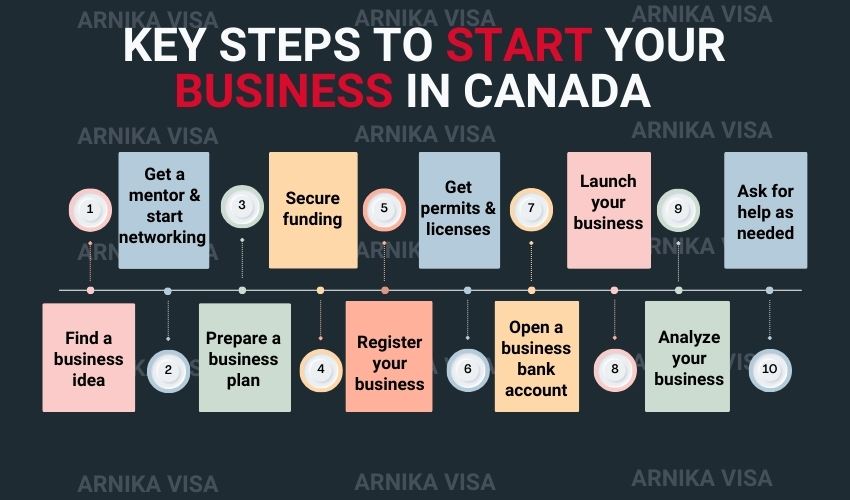
1.Choose Your Business Structure
This is a crucial decision that will shape your business’s future. The good news is you can decide on the business entity you want to establish. The typical structures are:
- Sole Proprietorship: Owned and operated by one person.
- Partnership: Owned by two or more individuals.
- Corporation: A separate legal entity owned by shareholders.
- Cooperative: Owned and operated by individuals for their mutual benefit.
2. Register Your Business
- Name Registration: Register a unique business name. Check for name availability using the federal or provincial business registries.
- Incorporation: If incorporating, register your corporation federally or provincially. Federal incorporation allows you to operate across Canada, while provincial incorporation limits you to one province.
3. Obtain Necessary Licenses and Permits
- Depending on your business type and location, you may need specific licenses and permits. For instance, a restaurant might need a food service permit, while a construction company might need a building permit. Check with local, provincial, and federal authorities to ensure compliance.
4. Create a Business Plan
- Develop a comprehensive business plan outlining your business objectives, market analysis, financial projections, and marketing strategies.
5. Secure Financing
- The journey to starting a business can be financially challenging, but there are numerous funding options available to you. Explore personal savings, bank loans, government grants, venture capital, or angel investors to find the one that suits your needs and aspirations.
6. Set Up Business Banking
- Open a business bank account to manage your finances separately from your accounts.
7. Understand Tax Obligations
- Register for a Business Number (BN) with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA).
- Register for Goods and Services Tax (GST)/Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) if your annual revenue exceeds CAD 30,000.
8. Set Up Accounting and Record-Keeping Systems
- Implement an accounting system to track income and expenses and manage your finances effectively.
9. Purchase Insurance
- Obtain business insurance to protect against risks and liabilities.
How Much Money Is Required To Start A Business In Canada?
Below is a detailed breakdown of the potential costs involved in starting a business in Canada:
1. Business Registration and Incorporation Fees:
- Sole Proprietorship: Registration fees range from CAD 60 to CAD 80, depending on the province.
- Corporation: Federal incorporation fees are CAD 200 (online) or CAD 250 (paper), while provincial incorporation fees range from CAD 300 to CAD 400.
2. Professional Fees
- Legal Fees: Hiring a lawyer for incorporation, contracts, and legal advice can cost between CAD 1,000 to CAD 3,000.
- Accounting Fees: The cost of setting up accounting systems and ongoing services can range from CAD 500 to CAD 2,000 annually.
3. Licenses and Permits:
- License and permit costs vary significantly by industry and location but typically range from CAD 100 to CAD 1,000.
4. Office Space and Utilities:
- Renting office space can cost from CAD 500 to CAD 5,000 per month, depending on the city and the size of the office.
- Utilities (electricity, water, internet, etc.) generally cost between CAD 150 and CAD 500 per month.
5. Insurance:
- Business insurance costs vary by industry and risk but typically range from CAD 500 to CAD 2,000 annually.
6. Marketing and Advertising:
- Initial marketing and advertising expenses can range from CAD 500 to CAD 5,000, depending on the marketing strategy and channels used.
7. Inventory and Equipment:
- Retail businesses may need CAD 5,000 to CAD 50,000 for initial inventory.
- Manufacturing or service-based businesses may require CAD 10,000 to CAD 100,000 for equipment and supplies.
8. Employee Salaries:
- Budget for at least three months of employee salaries. For example, if you have two employees with salaries of CAD 3,000 each per month, the cost for three months would be CAD 18,000.
Industry-Specific Costs
1. Retail:
- The initial investment for a small to medium-sized retail store, including inventory, leasehold improvements, and marketing, can range from CAD 50,000 to CAD 100,000.
2. Restaurants and Food Services:
- starting a business in Canada like a small restaurant can cost between CAD 100,000 to CAD 300,000, depending on location, size, and concept.
3. Tech Start-Ups:
- Tech start-ups often require significant investment in technology and development. Depending on the complexity of the product and development needs, initial costs can range from CAD 50,000 to CAD 500,000.
4. Franchises:
- The cost of buying a franchise in Canada as a foreignerng can vary widely. Some smaller franchises may require an initial investment of CAD 50,000 to CAD 100,000, while more extensive franchises, such as popular fast-food chains like Tim Horton, can require investments upwards of CAD 1 million or more.
Funding Options
1. Personal Savings
- Many entrepreneurs start their businesses using personal savings. This is often the most straightforward and quickest way to secure funding.
2. Bank Loans
- Traditional bank loans are a common funding source. Requirements include a solid business plan and a good credit history. Interest rates and terms vary.
3. Government Grants and Loans
- Canada offers grants and loans to support small businesses, such as the Canada Small Business Financing Program (CSBFP).
4. Venture Capital and Angel Investors:
- Venture capital and angel investors can provide significant funding for high-growth potential businesses in exchange for equity
5. Crowdfunding:
- Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow entrepreneurs to raise funds from the public by pre-selling products or offering other rewards.
How to Start a Small Business in Canada?
Starting a small business follows the same steps as starting a business in Canada but focuses on smaller-scale operations. Here are some specific tips:
- Identify Your Niche: Focus on a particular market segment or niche where you can provide unique value.
- Lean Startup Method: The lean startup approach minimizes initial costs. It involves starting with a minimal viable product (MVP) and gradually expanding.
- Home-Based Business: Consider starting from home to save on rent and utilities.
- Digital Presence: Build a solid online presence through a website and social media to reach a broader audience with minimal costs.
- Local Networking: Engage with local business communities and chambers of commerce to build relationships and gain insights.
Can I Start a Business in Canada Without PR?
Yes, starting a business in Canada without being a permanent resident is feasible. If you’re not a permanent resident, you can still start and run a business in Canada by obtaining a work permit. Here are some options:
- Entrepreneur Work Permit: C11 Work Permit is for those who can demonstrate significant benefit to the Canadian economy.
- Intra-Company Transfer: Intra Company Transfer, is for executives or managers of multinational companies transferring to a Canadian branch.
- Startup Visa Program: Start-Up Visa Canada program is for entrepreneurs with innovative business ideas supported by a designated organization. This can lead to permanent residency.
- Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs): Some provinces have business immigration streams named: Provincial Entrepreneur Program that allow you to start a business and eventually apply for PR.
Best Small Business to Start in Canada
- E-commerce Store: With the rise of online shopping, starting an e-commerce store selling niche products can be highly profitable.
- Food and Beverage: Specialty food shops, food trucks, and small cafes catering to local tastes and dietary trends.
- Tech Startup: Focus on app development, IT consulting, or software services. Canada’s tech industry is thriving.
- Health and Wellness: Businesses like yoga studios, fitness centers, or health coaching are in demand.
- Eco-Friendly Products: Sustainable and environmentally friendly products are increasingly popular.
- Home Renovation and Repair: The booming real estate market makes home improvement and maintenance services lucrative.
- Consulting Services: Offer expertise in business strategy, marketing, or human resources.
- Educational Services: Tutoring, online courses, and educational consulting are growing sectors.
Conclusion
The amount of money required to start a business in Canada varies greatly depending on the type and scale of the business. For instance, a small retail store might require an initial investment of CAD 50,000 to CAD 100,000, while a tech start-up could need CAD 50,000 to CAD 500,000 or more. On average, a small business owner should expect to invest at least CAD 10,000 to CAD 50,000 to cover initial costs. More substantial businesses or those in high-cost industries, such as technology or hospitality, may require significantly higher initial investments, ranging from CAD 100,000 to CAD 500,000 or more.
For a successful start, careful planning and thorough market research are not just important, they’re essential. These steps will help you determine the specific capital requirements for your business and secure the necessary funding. With the proper preparation and resources, starting a business in Canada can be profitable and rewarding. By understanding your market and planning your finances, you can enter the business world with confidence and a clear vision for success.
How Can We Help with Buy the Starting a business in Canada?
At Arnika Visa, as an RCIC (Regulated Canadian Immigration Consultant), we can assist our client with starting a business in Canada in several ways:
- Understanding Immigration Requirements: Determine whether our clients qualify for immigration programs like the Provincial Entrepreneur Program, C11 Work Permit, Intra Company Transfer, or the Start-Up Visa Program, as these may have particular restrictions related to business ownership.
- Researching business Options: We assist our clients in choosing a business that fits their budget, talents, and interests. We consider the initial investment, business reputation, market demand, and continuing support.
- Financial Planning and Investment: We help our clients comprehend the costs associated with purchasing a business, such as the initial business fees, royalties, and other recurring charges. We also assist them in developing a thorough business strategy and, if necessary, obtaining funding.
- Legal Compliance: Make sure our clients know all the contracts and legal responsibilities associated with owning a business, including disclosure paperwork, business agreements, and any laws that may apply to the company they have selected.
- Due Diligence: We help our clients perform extensive due diligence on the business opportunity, including examining financial records, speaking with existing businesses, and assessing the business’s reputation.
- Business Immigration Process: If our clients seek a visa or permanent residence due to their investment in a Canadian business, we assist them with the immigration process. This could entail putting together and filing applications, gathering supporting information, and communicating with immigration authorities.
- Networking and Support: To offer extra help and direction during the purchasing process, put our clients in touch with pertinent experts, including accountants, attorneys who specialize in business or business law, and other business owners.
- Post-Immigration Support: After our clients buy the business and move to Canada, you should still offer support and advice to help them launch and expand their company in their new nation.
We assist our clients in navigating the challenges of buying a business in Canada while guaranteeing compliance with business and immigration rules by providing thorough support throughout the process.




