Starting A Business In Canada For Foreigners
Are you interested in starting a business in Canada for foreigners? Entrepreneurs might find a wealth of chances in Canada when starting a firm. Initiating your business in Canada can be lucrative and fulfilling, as the country boasts a strong economy. With the help of this all-inclusive guide, you can quickly initiate your business venture in Canada. Learn how to prosper in Canada’s vibrant and friendly business environment, from navigating alternatives available to foreign entrepreneurs and business owners to seizing commercial opportunities.” This insight helps business owners and entrepreneurs learn about requirements and processes.
Immigration Options available for Starting a Business in Canada For Foreigners
Canada offers several immigration options for foreigners looking to start a business there. Here are some of the main pathways:
1. Start-Up Visa Program
This program is intended for creative company owners who can establish companies in Canada that can compete internationally and generate employment. To be eligible for a Canada startup visa, you must meet further eligibility requirements, obtain a letter of support from a qualified organization, and have a viable business plan.
2-Intra-Company Transfers
If you work as a senior executive or manager for a multinational corporation with a branch, affiliate, or subsidiary in Canada, you can be qualified for an intra company transfer Canada. This enables you to relocate to Canada to oversee or launch a branch, affiliate, or subsidiary of the business.
3-C11 Work Permits
Another choice available to foreigners wishing to establish a business in Canada is work visas, also called entrepreneur work permits or C11 work permit. Through this route, anyone can temporarily enter Canada to start or buy a business and actively oversee its operations. Entrepreneur Work Permits provide a versatile and reasonably priced solution for international business owners looking to test the Canadian market and launch their ventures.
4-Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs)
Numerous Canadian provinces provide specific immigration programs designed for entrepreneurs and company owners. These entrepreneurs immigration program differ from province to province, but they usually require you to start or invest in a business and fulfill specific requirements for employment creation, investment, and business management expertise.
5-Self-Employed Persons Program:
This program is designed for people who want to work for themselves in Canada and have appropriate experience in farming, sports, or cultural activities. To be eligible for self employed visa Canada, you must prove that you possess the knowledge, drive, and skills necessary to impact one of these sectors of the Canadian economy.
Immigration options have different qualifying standards, application procedures, and success criteria. Before proceeding, you must conduct in-depth research and evaluate which alternative best fits your business goals, credentials, and resources. Additionally, getting advice and support from an immigration lawyer or Regulated Immigration Consultant with experience in Canadian corporate immigration can be very beneficial.
What are three business structures to start in Canada?
1. Incorporation
Establishing your company as a corporation offers significant tax benefits and limited liability protection. A company name must be selected, incorporation papers must be filed with the government, and corporate rules must be followed.
2. Sole Proprietorship
Operating as a sole proprietorship is more accessible and only requires registering your company name with the authorities. Although it has fewer legal restrictions and offers flexibility, you are individually responsible for the business’s debts and responsibilities.
3. Partnership
When two or more people form a partnership, they share ownership and duties. In addition to registering the partnership with the relevant authorities, you’ll need to prepare a partnership agreement that outlines the conditions, obligations, and profit-sharing schedule.
What business options are available for entrepreneurs to start a business in Canada?
Business owners from other countries have several possibilities when starting a business in Canada for foreigners. These are a few typical paths:
- Incorporation: Foreign businesspeople can establish a company in Canada. To do this, the business must register with the Canadian government, either federally or provincially. A few advantages of incorporation are less liability and possible tax savings.
- Branch Office: Foreign businesses can open branches in Canada. This entails the foreign company being registered as an extraprovincial entity with the Canadian government. Canadian laws and functions govern a branch office as an extension of international business.
- Partnerships and Joint Ventures: International businesspeople can collaborate or form joint ventures with Canadian individuals or companies. This allows them to share risks and benefits and exploit local resources and experience.
- Franchising: Buying a Franchise in Canada as a Foreigner is an additional choice. This entails buying the authority to run a company using a well-known brand and business plan. When searching for a tested company idea, overseas entrepreneurs may find franchising a compelling alternative.
Foreign business owners should thoroughly investigate and weigh all available options before deciding on one, considering market potential, taxation, regulatory requirements, and the availability of resources and support systems. The procedure can be easier to understand if you speak with financial and business immigration experts knowledgeable about Canadian legislation.
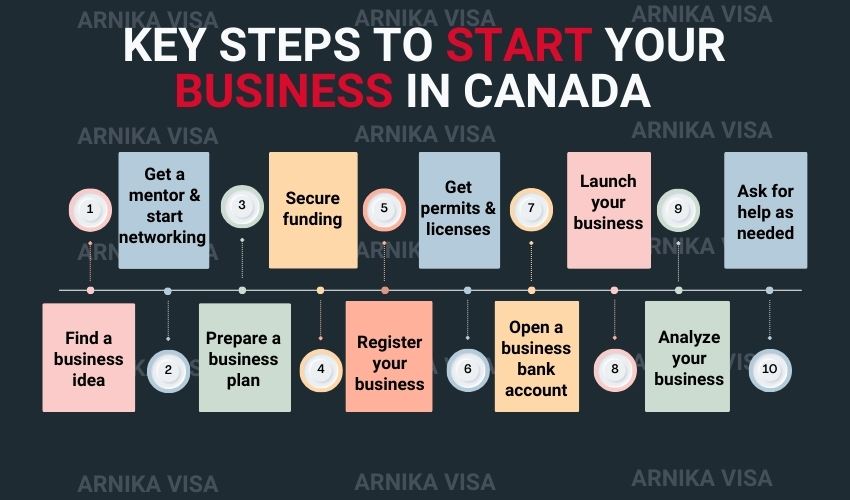
How to Start a Business in Canada?
Starting a business in Canada as a foreigner involves several steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Research and Planning:
- Determine the viability of your business idea by conducting market research.
- Examine the target market and the competition environment.
- Make a thorough business plan that includes your goals, target market, goods and services, promotional plans, and projected financials.
2. Choose a Business Structure:
- Choose a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or cooperative for your company’s legal structure.
- Selecting the appropriate business structure, consider ownership structure, liability protection, and tax implications.
3. Register Your Business:
- Obtain a business name registration from the relevant government agencies. This could entail registering the name with the local, state, or federal government after performing a name search to confirm availability.
- Depending on your business’s operations and location, you may need to obtain the required licenses or permissions. Jurisdiction and industry-specific requirements differ.
4. Obtain Business Permits and Licenses:
- Determine whatever licenses and permits you need to run your company lawfully. This could involve licenses particular to a specific industry, zoning permits, health permits, etc.
- Contact the appropriate federal, provincial, or local regulatory agencies to acquire the required licenses and permits.
5. Register for Taxes:
- Get a Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) business number (BN). This number is required for payroll deductions, corporate income tax, GST/HST registration, and other tax-related purposes.
- If your company’s yearly revenue exceeds the CRA’s threshold, register for the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) or Goods and Services Tax (GST).
6. Open a Business Bank Account:
- Open a different bank account to separate your professional and personal finances.
- Select a bank that fits the demands of your company and provides appropriate business banking services.
7. Set Up Accounting and Bookkeeping Systems:
- Put accounting and bookkeeping processes in place to monitor your company’s financial activities, costs, and income.
- To effectively manage your funds, consider using an accountant or accounting software.
8. Secure Funding:
- Establish your company’s financial needs and investigate your finance options, including grants, loans, venture capital, and bootstrapping.
- Create a thorough fundraising proposal and financial plan for possible lenders or investors.
9. Hire Employees (if necessary):
- Understand Canadian employment rules and regulations if your company needs staff.
- Create job descriptions, hold interviews, and select competent applicants to fill essential roles in your company.
10. Launch Your Business:
- Create a marketing strategy to advertise your company and draw clients.
- You can start a company and provide services to your intended clientele.
- To improve your company’s operations, track performance, get input, and make necessary corrections.
Starting a business in Canada for foreigners involves thorough preparation, following rules, and continuous management. Consulting with law, finance, and business experts guarantees a smooth and prosperous beginning for your entrepreneurial endeavours.
How to Register a Business in Canada?
Registering a business in Canada involves several steps. Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Select a Business Name: Verify that the name you have in mind for your enterprise is distinct and not being used by another organization within your legal jurisdiction.
- Choose Business Structure: Consider issues like tax ramifications and liability protection when choosing your company’s legal structure, such as a corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship.
- Register with the Federal or Provincial Government: Depending on your business structure and location, you can register your firm at the provincial or federal level. You can usually do this by mail or online.
- Obtain Required Permits and Licenses: Depending on your business operations and location, municipal, provincial, or federal authorities may require you to obtain permits or licenses. Find out what is needed in your particular location and sector.
- Register for Taxes: Get a business number (BN) from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) for tax purposes. Depending on your business’s operations and revenue, you might have to register for payroll deductions, GST/HST, and other tax-related programs.
- Apply for Workers’ Compensation, if necessary: If you employ people, you may need to register for workers’ compensation insurance with your province or territorial government.
- Open a Bank Account for Your Business: Open a separate bank account to separate your professional and personal finances.
- Observe Additional Regulatory Requirements: Depending on your line of work, you might have to abide by other legal requirements, such as environmental laws, industry-specific legislation, or health and safety standards.
- Renew Registrations Annually: Many of your business’s licenses, permits, and registrations must be renewed annually, so keep track of when they are due.
Because registration procedures and laws might differ between provinces and territories, it is crucial to research the particular requirements for your business kind and location. It is advisable to consult a lawyer, accountant, or business counsellor for expert guidance to guarantee adherence to all legal and regulatory mandates.
5 steps to start a business and move to Canada as a foreign national
- Research and Plan: Conduct a thorough business strategy and market research to confirm your idea. Investors and entrepreneurs can learn about Canadian immigration programs and their qualifying requirements by researching them.
- Choose a Business Structure: When choosing your company’s legal structure, such as incorporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship, consider tax and responsibility issues.
- Register Your Business: Obtain the required licenses, permits, and business number (BN) from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), then register your company with the relevant Canadian government agencies.
- Apply for Immigration: You may apply to Canada using one of the appropriate programs, such as the Provincial Nominee Program (PNP, C11 work Permit, ICT work Permit, or the Start-Up Visa Program. You must provide the necessary paperwork, evidence of your investment in or ownership of a firm, and evidence of your capacity to boost the country’s economy.
- Move and Launch: After your immigration application is accepted, move to Canada, set up shop, and begin your enterprise. Ensure that all Canadian rules and regulations are followed, and whenever necessary, seek the assistance of qualified consultants.
Starting A Business In Canada For Foreigners FAQs
What are the advantages of starting a business in Canada for foreigners?
Canada offers a stable economy, trade agreements that give access to international markets, fair rules, and a climate conducive to business for foreign entrepreneurs. The nation provides a highly qualified labour force, a multicultural community that encourages creativity, and financial assistance from the government through grants and tax breaks. Canada’s political stability, high standard of living, and rule of law make it a safe and alluring place for corporate investments. International entrepreneurs who launch a business in Canada have a bright future ahead of them, full of opportunities for success and expansion in a friendly and vibrant business environment.
What are the best small business to start in canada?
Canada’s varied economy fosters several thriving trim business options. The growth of e-commerce has created niches for online retailers. There is a growing demand for health and wellness services such as yoga studios and health food cafes. Digital marketing agencies serve businesses that require an online presence. Services for home repair and renovation take advantage of the expanding housing industry. Because Canadians are environmentally sensitive, there is a promising market for eco-friendly products. Entrepreneurs need to evaluate their abilities, passions, and local market needs to succeed. In Canada’s changing business environment, they can uncover profitable opportunities by studying extensively and playing to their strengths. So, the above industries are the best small business in Canada.
Can I open a business in Canada without PR?
You don’t need a permanent residence to launch a business in Canada. They can select from various legal forms, file taxes, register with the appropriate authorities, and take residency restrictions into account. It’s essential to open a company bank account and follow immigration regulations. Professional counsel is advised to navigate legal and regulatory complications effectively.
How much does it cost to register a company in Canada as a foreigner?
Depending on the province or territory you want to register in and the type of business structure you want, different costs are associated with forming a foreign company in Canada. The price might be anything from $200 to $1000 or more. For instance, registering a business provincially can cost anywhere from $300 to $1000 or more, whereas creating a federal corporation usually costs between $200 and $400. Name searches, permits, and other formalities may incur additional costs. To find out the precise costs associated with this, depending on your situation and your organization’s needs, it is best to speak with legal or business experts.
What business can immigrants do in Canada?
Canada offers many business opportunities for immigrants, including the food and beverage industry, retail, professional services, cultural consultancy, tourism, home-based businesses, construction trades, health and wellness, and technology startups and franchising. In addition to providing professional consulting, accounting, and IT services, they can open eateries and retail establishments. Cultural competence can be used for heritage tours, event organizing, and language translation. There are also opportunities for hotels, tour companies, and travel agents in the tourist industry. Viable choices include home-based enterprises, wellness and health services, and skills like building. Franchise opportunities and technology companies provide more avenues for immigrant entrepreneurs to thrive in Canada’s dynamic business environment.
Is it difficult to start a business in Canada?
Although there are obstacles to starting a business in Canada, the country is generally regarded as having a supportive business environment for entrepreneurs. The procedure can be intimidating for some because it entails managing laws, tax obligations, and market rivalry. However, Canada provides tools to help companies, including government initiatives, incubators, accelerators, and networking opportunities. Different regions and industries have other access to capital, skilled labour, and market demand. Even though there are obstacles, many entrepreneurs in Canada are successful in starting and expanding their companies by meticulous planning, diligence, and determination.
What are most profitable business in Canada?
Specific industries in Canada have an exceptionally high potential for profitability. The demand for rental homes and a robust housing market drive the real estate industry’s profitability. Software development, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence opportunities are available in the rapidly expanding technology sector. The elderly population is catered to by healthcare services, with home care and medical equipment in high demand. Canada’s dedication to sustainability fosters the growth of renewable energy enterprises, especially in solar and wind power fields. In addition, as online purchasing expands, e-commerce keeps growing. The dynamic business landscape of Canada necessitates strategic planning, market demand, and experience for any sector to succeed. So, the above industries are the most profitable business in Canada.
What Do I need to know about business in Canada?
Understanding essential elements, including legal and regulatory requirements, tax obligations, market dynamics, and cultural quirks, is necessary for doing business in Canada. Learn about the various business structures, such as sole proprietorship or incorporation, and make the necessary registrations. Respect tax rules and secure all required licenses and permits. To create a competitive strategy, study your competition and target market. Success requires networking, forming relationships, and adjusting to Canada’s multicultural atmosphere. To overcome obstacles and seize opportunities, stay current on market developments and seek assistance from sources such as government initiatives, trade associations, and expert consultants.
how to start a small business in Canada?
To start a small business in Canada, you should first determine your target market and niche through careful planning and research. Select an appropriate legal framework, register your company name, and secure the required licenses and permissions. Create a thorough business plan that details your objectives, budget, and approach to marketing. Obtain funding via government initiatives, loans, or personal savings. Establish operations, such as choosing a site and building connections with suppliers. Use a variety of avenues to market your company efficiently. Ensure all regulations are followed, and think about employing staff where necessary. Start your company, then as it expands, and you navigate the Canadian business environment, modify and improve your tactics.
How Can We Help with Starting a Business In Canada?
At Arnika Visa, as an RCIC (Regulated Canadian Immigration Consultant), we can assist our client with starting a business in Canada in several ways:
- Understanding Immigration Requirements: Determine whether our clients qualify for immigration programs like the Provincial Entrepreneur Program, C11 Work Permit, Intra Company Transfer, or the Start-Up Visa Program, as these may have particular restrictions related to business ownership.
- Researching business Options: We assist our clients in choosing a business that fits their budget, talents, and interests. We consider the initial investment, business reputation, market demand, and continuing support.
- Financial Planning and Investment: We help our clients comprehend the costs associated with purchasing a business, such as the initial business fees, royalties, and other recurring charges. We also assist them in developing a thorough business strategy and, if necessary, obtaining funding.
- Legal Compliance: Make sure our clients know all the contracts and legal responsibilities associated with owning a business, including disclosure paperwork, business agreements, and any laws that may apply to the company they have selected.
- Due Diligence: We help our clients perform extensive due diligence on the business opportunity, including examining financial records, speaking with existing businesses, and assessing the business’s reputation.
- Business Immigration Process: If our clients seek a visa or permanent residence due to their investment in a Canadian business, we assist them with the immigration process. This could entail putting together and filing applications, gathering supporting information, and communicating with immigration authorities.
- Networking and Support: To offer extra help and direction during the purchasing process, put our clients in touch with pertinent experts, including accountants, attorneys who specialize in business or business law, and other business owners.
- Post-Immigration Support: After our clients buy the business and move to Canada, you should still offer support and advice to help them launch and expand their company in their new nation.
We assist our clients in navigating the challenges of buying a business in Canada while guaranteeing compliance with business and immigration rules by providing thorough support throughout the process.
Starting a business in Canada Related Articles






I plan to incorporate an IT company, start my own business, and apply for a C11 work permit as CEO. Let me know how to proceed.
“Incorporate your IT company in Canada. Developing a strong business plan shows significant benefits for Canadians or Canada. Apply for a C11 work permit as CEO. Ensure compliance with immigration regulations. Seek professional guidance from an expert on C11 visas if needed. Good luck!”
I am looking for assistance with a C11 work permit. The Business is an Australian-Canadian consultation agency. I am an Australian business consultant. The Canadian branch was established in November 2022. I am currently holding an IEC visa expiring in late September 2024. Please let me know how to apply.
Explore extending your stay or transitioning to a proper Canadian work permit. Contact us for personalized guidance on your application process.
I am on a visitor visa in Canada. I am a qualified engineer with more than 25 years of experience, and I am looking for a C11 visa to starting abusiness as an entrepreneur and settle here.
I have a few questions regarding starting a business in Canada. I need to know the procedure and how it works. Please let me know if we can set up an online meeting. Also, is there any opportunity to buy a partnership?
To buy an established business, research, conduct due diligence, negotiate terms, seek legal and financial advice, and finalize the sale. For the C11 visa, ensure eligibility, prepare documents, apply, undergo assessment, and receive the visa to start or buy a business in Canada if approved. Fortunately, all of our consultation sessions are held online .meetings.
We are operating a tour and travel business here in Pakistan. We are interested in getting PR over this business. I have studied the details of the c11 work permit category on your website. I am interested in the same to start a business in Canada. So please send the details.
For your travel agency business plan, include a business description, market analysis, marketing and sales plans, operational details, team overview, financial projections, and risk analysis. Is there any specific section of the business plan you’d like to focus on or need further assistance with? Let us know, and we’ll be happy to help!
To apply for Canadian PR through the C11 work permit for your tour business, prepare the required documents and apply for your C11 visa. Get the work permit, operate your business in Canada, then follow immigration procedures to apply for PR through Express Entry or a Provincial Nominee Program.
I want to start a business in Canada. I have two industries in mind: event decorating and pet care/training. Hopefully, I have reached the right agency to point me in the right direction.
Yes, you’ve reached the right place. We can guide you through the process of buying a business in Canada. Please provide more details about your preferred industries, investment amount, and any specific business you’re considering.
I have investments to start a business in Canada. Can you apply my file?
Yes, We can help you apply for a business visa in Canada. To proceed with your application, please provide details about your investment, business plan, and any relevant documents.
I have a diploma in electronic with a license for 15 years and have 3 technical degrees in plumbing. Am I eligible to start my business in Canada? Please guide me.
Yes, you may be eligible to start a business in Canada. Depending on your background and business plans, programs like the Start-Up Visa or provincial entrepreneur programs might suit you. Consult a business immigration lawyer to explore your options and receive personalized guidance.
I want to start a small business in Canada, in the field of street food sales. What visa do I need to apply for?
You can apply for a C11 Work Permit or explore provincial options under the PNP Entrepreneur streams. Both require a solid business plan and demonstrate economic benefits to Canada.